
- L298N MOTOR DRIVER SERVO MOTOR ARDUINO HOW TO
- L298N MOTOR DRIVER SERVO MOTOR ARDUINO FULL
- L298N MOTOR DRIVER SERVO MOTOR ARDUINO CODE
Interfacing L298N DC Motor Driver Module with ESP8266 NodeMCU.

L298N MOTOR DRIVER SERVO MOTOR ARDUINO HOW TO
Next, the motor changes the direction and is driven in slow mode for 5 seconds as well as in fast mode for 5 seconds.In this user guide, we will learn how to control a DC motor with Raspberry Pi Pico in MicroPython by using an L298N motor driver. Then, the motor drives in fast mode for 5 seconds. Naturally, the direction of the motor also depends on the direction you mounted the motor as well as on how you connected the motors pin to the module’s pins 13 and 14. In the loop function, the motor is driven forward in slow mode for five seconds. Please note, that the motor will not work if the values are too low. The higher the value (0 to 255), the higher the speed of the motor. The functions slow() and fast() write an analog value to the PWM pin that is connected to ENB.
L298N MOTOR DRIVER SERVO MOTOR ARDUINO CODE
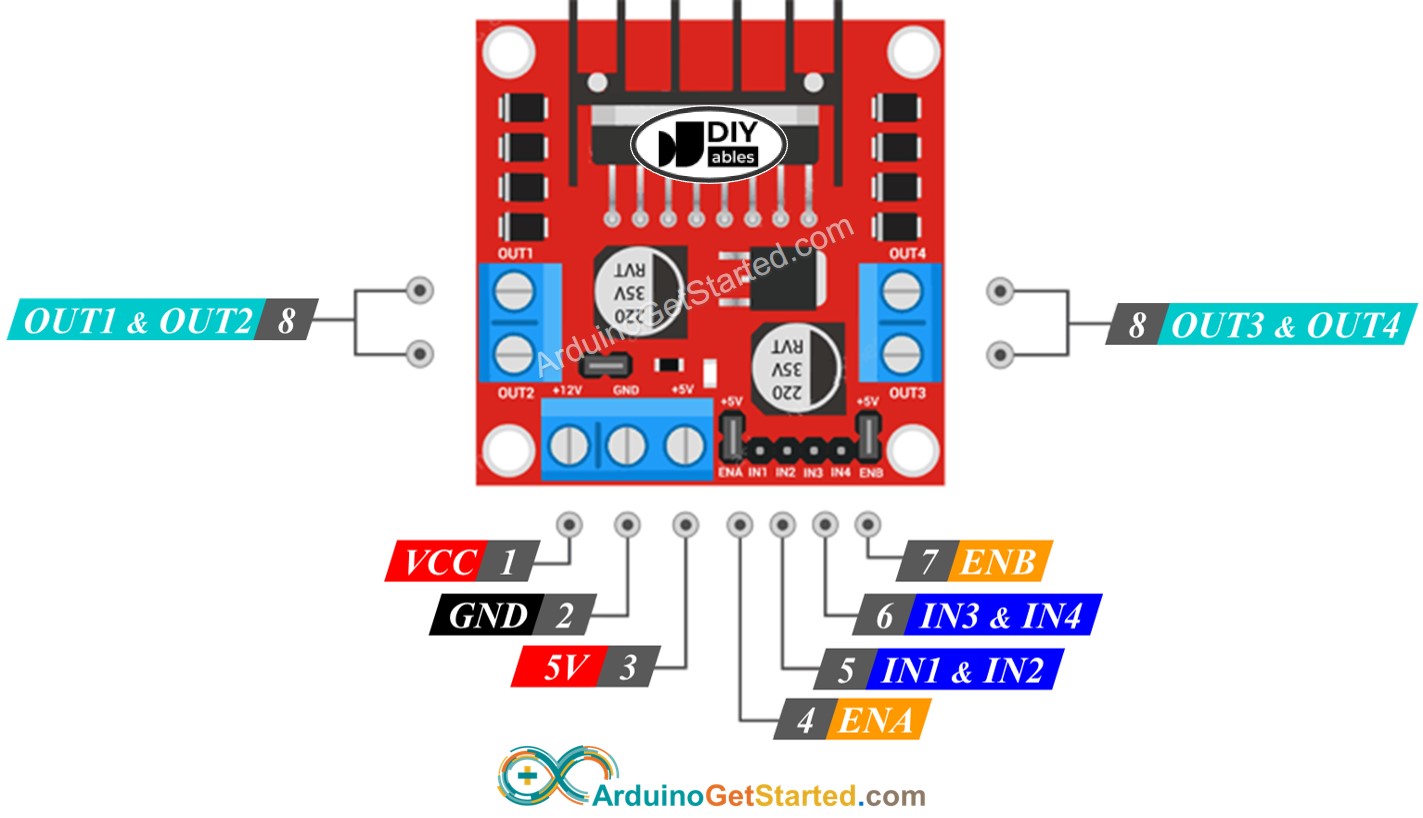
This source code drives the motor in four different states: Forward in slow and fast mode as well as backward in slow and fast mode. These pins are used to control the direction of the DC motor (IN3=HIGH/IN4=LOW or IN3=LOW/IN4=HIGH).Īs a final step, the module’s output pins for the second motor (pin 13 and 14) are connected to the DC motor.Įxample source code: Picture of the setup. Then, the Arduino’s pins 7 and 8 is connected to the module’s pins IN3 and IN4, respectively. This connection is used to control the speed of the motor and, therefore, using one of the Arduino’s PWM-enabled pins is required. The Arduino’s pin 6 is connected to the ENB pin of the module. An Arduino is wired to an L298N module to control a DC motor. Therefore, the breadboard’s “-” line is also connected to one of the Arduino’s GND pins.

It is important that the L298N module and the Arduino share the same GND. The breadboard’s “+” line (Vcc) is connected to pin 1 of the L298N module. The breadboard’s “-” line (GND) is connected to pin 2 of the L298N module. Then, the power jack socket is connected to the breadboard. In this tutorial, a USB Power boost (5V-to-9V) is used in combination with a DC power jack socket. Therefore, a second voltage supply of 9V is used. As the L298N module drops the voltage by more than 2V, the 5V voltage supply (USB) of the Arduino can’t be used. The used DC motor has an operating voltage of 3V up to 12V. In order to power the DC motor, two voltage supplies with different voltages are needed. The L298N module can also be used to control two motors with different directions and speeds. In this tutorial, the L298N Dual Motor Controller is used to control a single DC motor with the Arduino Uno. Moreover, most DC motors need more power than the Arduino could provide.
L298N MOTOR DRIVER SERVO MOTOR ARDUINO FULL
However, many DC motors need more than 5V, especially when they are supposed to move on full speed. In order to control a DC motor with the Arduino Uno, a motor controller module is required. Such module is needed, for various reasons: For example, the Arduino can’t power DC motors with a voltage higher than 5V. If the jumper is enabled, motor 2 will run on full speed. If the jumper is enabled, motor 1 will run on full speed.ġ2 (ENB): One of Arduino’s PWM pins can be connected (to the lower pin) to control the speed of motor 2. for driving an Arduino)ħ (ENA): One of Arduino’s PWM pins can be connected (to the lower pin) to control the speed of motor 1. Pin description (for controlling DC motors):ģ: If jumper enabled, 5V output on pin 6(e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
